The problem of aviation data authenticity
The complexities added by data in the aviation industry are tremendous. Let’s look at some of the data points that are collected by every operator & MRO. On average, every aircraft configuration has about 6 Million parts that need to be tracked with their associated maintenance and component programs. Apart from tracking the part and aircraft maintenance history, service bulletins (SBs), and airworthiness directives that an aircraft needs to comply with, results in a plethora of data.
This data is housed on multiple systems which vary from one organization to another. When there is a decision to buy or sell or add parts to inventory, a lot of time and effort is spent in validating the authenticity of this data by organizations that involve many purchasers specialized in purchasing and inspecting these parts to validate the data. This is also one of the reasons why the supply chain side of aviation parts is long and cumbersome. There is an innate requirement to validate data on any of the conventional systems.
Why Only Blockchain for aviation?
Blockchain, with its innate properties of decentralization and immutability, holds the solution to the complex data problem. First and foremost, by storing this critical aircraft data on the blockchain, it becomes impossible to tamper with the records. The part certifications (8130/EASA Form 1) generated on a blockchain network becomes so much more valuable for the buyers and regulatory authorities as it guarantees authenticity.
This brings about a unique opportunity for operators and MRO officers to securely share data - a thing that was frowned upon earlier due to security concerns.
The immediate incentive to move to blockchain might be immutability and the trust that it brings to data, but this is just the tip of the iceberg. With a rise in large-scale adoption, it enables organizations to be pioneers and leaders in defining new and secure ways to transact with their value chain.
Aviation use cases at a glance
Blockchain can be used for a multitude of things and depends on the problem each organization is looking to solve. There is a general misconception that there should be multiple parties involved to set up a blockchain network, which is untrue. Here are a few ways in which aviation organizations can deploy their own blockchains centered around 3 themes
- Trust
- Traceability
- Transactional Agreement (Consensus)
Trust
Designed to bring trust to the data stored and shared, some areas where trust-based blockchain solutions would play a major role are –
Parts and aircraft Configuration
Creating and replicating a digital twin of the aircraft and part configuration gives detailed insights on the higher and lower assemblies. It would also help organizations keep track of any specific modifications done to the delivered configurations accurately. Organizations can then keep an efficient track of the modifications, compliances to specific service bulletins, and ownership change of particular sub-assemblies, and more. This information stands critical during regulatory reporting and selling or buying of parts.
Aircraft Maintenance Program Management
The compliance of both part and aircraft maintenance programs can be managed on a blockchain network. The compliance to specific types of tasks (for example - disallowing the same mechanic to work on both engines of the aircraft), recording inspection findings, requesting follow-up checks, recommendations for shop visits are some of the critical functions that can be managed on a blockchain.
Aircraft Reliability Program
Information pertaining to the aircraft reliability program, inferences of the statistical analysis, and the recording of events to recommend changes in the maintenance programs can also be stored on blockchain to guarantee immutability.
Traceability
Gaining trust in the data put into a blockchain network simplifies the journey to track the history of parts, maintenance, and warranty. A few use cases where the property of traceability takes centerstage include
Back to Birth Traceability
Aircraft components categorized as “Rotables” have infinite life as they are components that can be repaired an infinite number of times and there is very little value in scrapping them. While the lower assemblies are scrapped and changed, the higher assembly is hence left intact. These parts are one of the main reasons why back-to-birth traceability becomes important paving the need to store the relevant maintenance records, ownership history, and the changes on an immutable ledger.
Repair Order management & Loan Order Management
Repair Order
Repair Orders created in the event of certain defects, maintenance activities requested on parts, requests put in by the Operator/MRO, and technical records of components can be maintained on a blockchain network. The subsequent maintenance carried out and the compliance reports can also be stored on the network ensuring transparency and traceability
Loan Order
Multiple complex transactions take place between operators and MROs, loan order being one. The terms of the loan given out can be maintained on an immutable ledger, along with all the technical records of the component.
Warranty Management
Warranty management is an area where there is huge revenue leakage for organizations. The terms of the warranty and the payouts can be maintained on the blockchain network
Transactional Agreements
Blockchain also has another strong suite called smart contracts that can be used to ensure and automatically validate transactional agreements when there are multiple parties involved. This is the underlying factor that brings consensus to a large group. Here’s one such example:
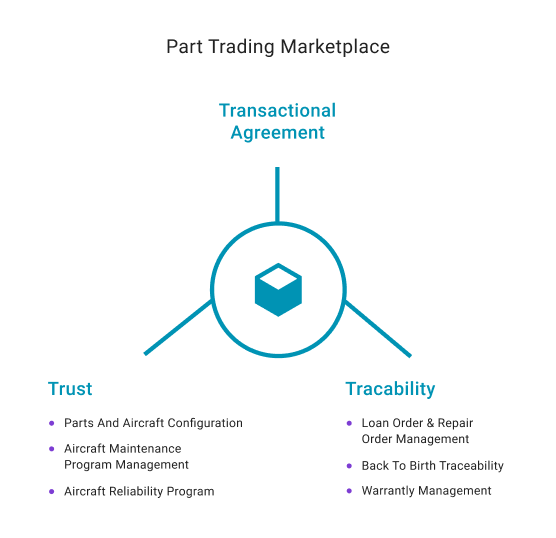
Part trading market place
A part trading marketplace is one of the best examples of seeing blockchain in action as it involves multiple parties like operators, MROs, and supply chain operators who can be brought together with an agreement in place also called a smart contract. Significant efficiency can be realized in how the parts are traded and how information is shared among the multiple parties while also recording the consensus and the technical information shared amongst each other to avoid conflicts.
Give your air business the Blockedge
The fear of the unknown is one of the major challenges associated with blockchain that hinders it from going mainstream in organizations. As the technology is still at a very nascent stage, there is a common misconception that it would be very expensive and tedious to build these blockchain nodes and manage them over time. This is, however, partially true if setting up nodes and blockchain networks is done manually, which is one of the driving forces for us to build Blockedge.
Blockedge is an infrastructure automation platform that facilitates blockchain adoption with Zero Coding! Blockedge not only helps build blockchain networks but also manages the ongoing operations. Organizations can then focus on their business while Blockedge manages their blockchain infrastructure.
We understand blockchain is continually evolving and there is a lot of complexity in building and managing networks, that is why we have abstracted the complexity to a simple user interface. As a business owner, you can then build blockchain nodes, networks, consortia, and manage multiple networks, without worrying about the infrastructure overheads.
What AWS has done to Cloud computing, we’re bringing to blockchain with Blockedge!